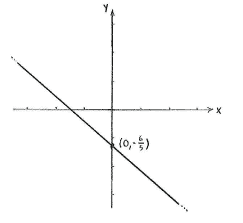Solution 2.2:6c
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
(Difference between revisions)
m |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The point of intersection is that point which satisfies the equations of both lines | The point of intersection is that point which satisfies the equations of both lines | ||
| + | {{Displayed math||<math>4x+5y+6=0\qquad\text{and}\qquad x=0\,\textrm{.}</math>}} | ||
| - | <math> | + | Substituting <math>x=0</math> into <math>4x+5y+6=0</math> gives |
| - | + | ||
| - | <math> | + | |
| - | + | {{Displayed math||<math>4\cdot 0+5y+6=0\quad\Leftrightarrow\quad y=-\frac{6}{5}\,\textrm{.}</math>}} | |
| - | <math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | This gives the point of intersection as <math>\bigl(0,-\tfrac{6}{5}\bigr)</math>. | ||
| - | <math>4\centerdot 0+5y+6=0\ \Leftrightarrow \ y=-\frac{6}{5}</math> | ||
| - | + | <center>[[Image:2_2_6_c.gif|center]]</center> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | < | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[Image:2_2_6_c.gif|center]] | + | |
| - | + | ||
Current revision
The point of intersection is that point which satisfies the equations of both lines
| \displaystyle 4x+5y+6=0\qquad\text{and}\qquad x=0\,\textrm{.} |
Substituting \displaystyle x=0 into \displaystyle 4x+5y+6=0 gives
| \displaystyle 4\cdot 0+5y+6=0\quad\Leftrightarrow\quad y=-\frac{6}{5}\,\textrm{.} |
This gives the point of intersection as \displaystyle \bigl(0,-\tfrac{6}{5}\bigr).