Solution 4.2:3d
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
(Difference between revisions)
m (Lösning 4.2:3d moved to Solution 4.2:3d: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | {{ | + | In order to get an angle between |
| - | < | + | <math>0</math> |
| - | {{ | + | and |
| + | <math>\text{2}\pi </math>, we subtract | ||
| + | <math>\text{2}\pi </math> | ||
| + | from | ||
| + | <math>{7\pi }/{2}\;</math> | ||
| + | , which also leaves the cosine value unchanged | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\cos \frac{7\pi }{2}=\cos \left( \frac{7\pi }{2}-2\pi \right)=\cos \frac{3\pi }{2}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | When we draw a line which makes an angle | ||
| + | <math>{3\pi }/{2}\;</math> | ||
| + | with the positive | ||
| + | <math>x</math> | ||
| + | -axis, we get the negative | ||
| + | <math>y</math> | ||
| + | -axis and we see that this line cuts the unit circle at the point | ||
| + | <math>\left( 0 \right.,\left. -1 \right)</math>. The | ||
| + | <math>x</math> | ||
| + | -coordinate of the intersection point is thus | ||
| + | <math>0</math> | ||
| + | and hence | ||
| + | <math>\cos {7\pi }/{2}\;=\cos {3\pi }/{2}\;=0</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
[[Image:4_2_3_d.gif|center]] | [[Image:4_2_3_d.gif|center]] | ||
Revision as of 12:06, 28 September 2008
In order to get an angle between \displaystyle 0 and \displaystyle \text{2}\pi , we subtract \displaystyle \text{2}\pi from \displaystyle {7\pi }/{2}\; , which also leaves the cosine value unchanged
\displaystyle \cos \frac{7\pi }{2}=\cos \left( \frac{7\pi }{2}-2\pi \right)=\cos \frac{3\pi }{2}
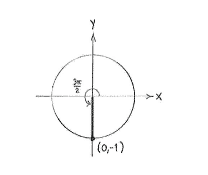
When we draw a line which makes an angle
\displaystyle {3\pi }/{2}\;
with the positive
\displaystyle x
-axis, we get the negative
\displaystyle y
-axis and we see that this line cuts the unit circle at the point
\displaystyle \left( 0 \right.,\left. -1 \right). The
\displaystyle x
-coordinate of the intersection point is thus
\displaystyle 0
and hence
\displaystyle \cos {7\pi }/{2}\;=\cos {3\pi }/{2}\;=0