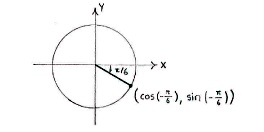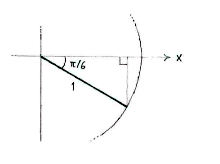Solution 4.2:3f
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
(Difference between revisions)
(Ny sida: {{NAVCONTENT_START}} <center> Bild:4_2_3f-1(2).gif </center> {{NAVCONTENT_STOP}} {{NAVCONTENT_START}} <center> Bild:4_2_3f-2(2).gif </center> {{NAVCONTENT_STOP}}) |
m |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | The point on the unit circle which corresponds to the angle <math>-\pi/6</math> lies in the fourth quadrant. | |
| - | < | + | |
| - | {{ | + | [[Image:4_2_3_f1.gif||center]] |
| - | {{ | + | |
| - | < | + | As usual, <math>\cos (-\pi/6)</math> gives the ''x''-coordinate of the point of intersection between the angle's line and the unit circle. In order to determine this point, we introduce an auxiliary triangle in the fourth quadrant. |
| - | { | + | |
| + | [[Image:4_2_3_f2.gif||center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | We can determine the edges in this triangle by simple trigonometry and then translate these over to the point's coordinates. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| width="100%" | ||
| + | |width="50%" align="center"|[[Image:4_2_3_f3.gif]] | ||
| + | |width="50%" align="left"|<math>\begin{align}\text{opposite} &= 1\cdot\sin\frac{\pi}{6} = \frac{1}{2}\\[5pt] \text{adjacent} &= 1\cdot\cos\frac{\pi}{6} = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\end{align}</math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The coordinates of the point of intersection are <math>(\sqrt{3}/2,-1/2)</math> and in particular <math>\cos (-\pi/6) = \sqrt{3}/2\,</math>. | ||
Current revision
The point on the unit circle which corresponds to the angle \displaystyle -\pi/6 lies in the fourth quadrant.
As usual, \displaystyle \cos (-\pi/6) gives the x-coordinate of the point of intersection between the angle's line and the unit circle. In order to determine this point, we introduce an auxiliary triangle in the fourth quadrant.
We can determine the edges in this triangle by simple trigonometry and then translate these over to the point's coordinates.
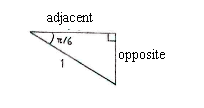
| \displaystyle \begin{align}\text{opposite} &= 1\cdot\sin\frac{\pi}{6} = \frac{1}{2}\\[5pt] \text{adjacent} &= 1\cdot\cos\frac{\pi}{6} = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\end{align} |
The coordinates of the point of intersection are \displaystyle (\sqrt{3}/2,-1/2) and in particular \displaystyle \cos (-\pi/6) = \sqrt{3}/2\,.