Solution 4.4:2b
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
(Difference between revisions)
m (Robot: Automated text replacement (-[[Bild: +[[Image:)) |
m |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
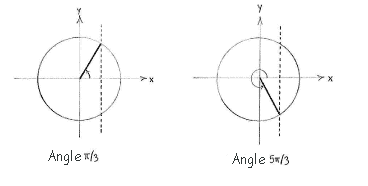
| - | + | The equation <math>\cos x= 1/2</math> has the solution <math>x=\pi/3</math> in the first quadrant, and the symmetric solution <math>x = 2\pi -\pi/3 = 5\pi/3</math> in the fourth quadrant. | |
| - | < | + | |
| - | + | ||
[[Image:4_4_2_b.gif|center]] | [[Image:4_4_2_b.gif|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | If we add multiples of <math>2\pi</math> to these two solutions, we obtain all the solutions | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Displayed math||<math>x = \frac{\pi}{3}+2n\pi\qquad\text{and}\qquad x = \frac{5\pi }{3}+2n\pi\,,</math>}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | where ''n'' is an arbitrary integer. | ||
Current revision
The equation \displaystyle \cos x= 1/2 has the solution \displaystyle x=\pi/3 in the first quadrant, and the symmetric solution \displaystyle x = 2\pi -\pi/3 = 5\pi/3 in the fourth quadrant.
If we add multiples of \displaystyle 2\pi to these two solutions, we obtain all the solutions
| \displaystyle x = \frac{\pi}{3}+2n\pi\qquad\text{and}\qquad x = \frac{5\pi }{3}+2n\pi\,, |
where n is an arbitrary integer.