Solution 4.4:5c
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
(Difference between revisions)
m |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
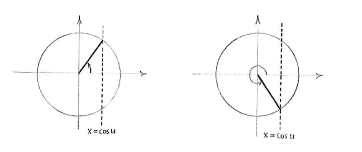
| - | For a fixed value of | + | For a fixed value of ''u'', an equality of the form |
| - | + | ||
| + | {{Displayed math||<math>\cos u=\cos v</math>}} | ||
| - | + | is satisfied by two angles ''v'' in the unit circle, | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | is satisfied by two angles | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | in the unit circle | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | {{Displayed math||<math>v=u\qquad\text{and}\qquad v=-u\,\textrm{.}</math>}} | ||
[[Image:4_4_5_c.gif|center]] | [[Image:4_4_5_c.gif|center]] | ||
| - | This means that all angles | + | This means that all angles ''v'' which satisfy the equality are |
| - | + | ||
| - | which satisfy the equality are | + | |
| + | {{Displayed math||<math>v=u+2n\pi\qquad\text{and}\qquad v=-u+2n\pi\,,</math>}} | ||
| - | + | where ''n'' is an arbitrary integer. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | where | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | is an arbitrary integer. | + | |
Therefore, the equation | Therefore, the equation | ||
| - | + | {{Displayed math||<math>\cos 5x=\cos (x+\pi/5)</math>}} | |
| - | <math>\cos 5x=\cos | + | |
| - | + | ||
has the solutions | has the solutions | ||
| - | + | {{Displayed math||<math>\left\{\begin{align} 5x&=x+\frac{\pi}{5}+2n\pi\quad\text{or}\\[5pt] 5x &= -x-\frac{\pi}{5}+2n\pi\,\textrm{.}\end{align}\right.</math>}} | |
| - | <math>5x=x+\frac{\pi }{5}+2n\pi | + | |
| - | or | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | If we collect | + | If we collect ''x'' onto one side, we end up with |
| - | + | ||
| - | onto one side, we end up with | + | |
| + | {{Displayed math||<math>\left\{\begin{align} | ||
| + | x &= \frac{\pi}{20} + \frac{n\pi}{2}\,,\\[5pt] | ||
| + | x &= -\frac{\pi }{30}+\frac{n\pi}{3}\,, | ||
| + | \end{align}\right.</math>}} | ||
| - | + | where ''n'' is an arbitrary integer. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | an arbitrary integer | + | |
Current revision
For a fixed value of u, an equality of the form
| \displaystyle \cos u=\cos v |
is satisfied by two angles v in the unit circle,
| \displaystyle v=u\qquad\text{and}\qquad v=-u\,\textrm{.} |
This means that all angles v which satisfy the equality are
| \displaystyle v=u+2n\pi\qquad\text{and}\qquad v=-u+2n\pi\,, |
where n is an arbitrary integer.
Therefore, the equation
| \displaystyle \cos 5x=\cos (x+\pi/5) |
has the solutions
| \displaystyle \left\{\begin{align} 5x&=x+\frac{\pi}{5}+2n\pi\quad\text{or}\\[5pt] 5x &= -x-\frac{\pi}{5}+2n\pi\,\textrm{.}\end{align}\right. |
If we collect x onto one side, we end up with
| \displaystyle \left\{\begin{align}
x &= \frac{\pi}{20} + \frac{n\pi}{2}\,,\\[5pt] x &= -\frac{\pi }{30}+\frac{n\pi}{3}\,, \end{align}\right. |
where n is an arbitrary integer.