Solution 4.4:2c
From Förberedande kurs i matematik 1
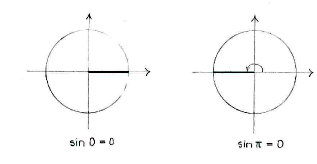
There are two angles in the unit circle, \displaystyle x=0\text{ } and \displaystyle x=\pi , whose sine has a value of zero.
We get the full solution when we add multiples of \displaystyle 2\pi ,
\displaystyle x=0+2n\pi
and
\displaystyle x=\pi +2n\pi ,
where \displaystyle n is an arbitrary integer.
NOTE: Because the difference between \displaystyle 0 and \displaystyle \pi is a half turn, the solutions are repeated every half turn and they can be summarized in one expression:
\displaystyle x=0+n\pi
where
\displaystyle n
is an arbitrary integer.