3. Other types of force
From Mechanics
| Theory | Exercises | Video |
Key Points
For a body or group of bodies in equilibrium the sum of the forces is zero in any direction.
Tensions exist in ropes and act along the rope towards the centre.
Tensions and thrusts exist in rods.
Friction exists where rough surfaces are in contact.

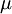 R
R
Here
The coefficient of friction is 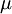
The normal reaction force is
If only one surface is flat the normal reaction force is perpendicular to that surface.
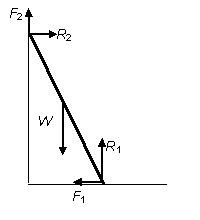
Draw a diagram to show the forces acting on a ladder leaning against a wall.
Solution
Note it has been assumed that the wall is vertical and the ground horizontal
The coefficient of friction between a crate, of mass 50 kg, and the floor is 0.7. Find the magnitude of the friction force acting on the crate if it is on a horizontal surface and;
a) no horizontal force acts on the crate,
b) a horizontal force of 80 N acts on the crate,
c) A horizontal force of 400 N acts on the crate.
Solution
In all of the cases described above, the same vertical forces act on the crate.
So in all of these cases
Using the friction inequality gives,

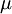 RF
RF 0.7
0.7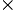 490F
490F 343
343
So the maximum friction force in this situation is 343 N.
a) If no horizontal force acts on the crate there will be no friction force.
b) If a horizontal force of 80 N acts on the crate the forces will be as shown in the diagram.
In this case
In this case
c) The forces are now as shown in the diagram.
A force of 400 N would be needed to
produce equilibrium. As this is greater
than the maximum friction,
In this case there is a resultant force of 57 N to the right.
The diagram shows a block that is at rest on a horizontal plane. Two light ropes, attached to the block pass over pulleys and are also attached to masses as shown in the diagram. Find the tension in each rope and the friction between the block and the plane and an inequality that the coefficient of friction must satisfy.
Solution
Considering the 8 kg mass, which is in equilibrium gives,
Considering the 12 kg mass, which is also in equilibrium gives,
Now consider the block on the plane, which is also in equilibrium.
Vertically:
Horizontally
Using the values for the two tensions gives,
Using the friction inequlity

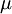 R
R

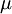
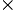 196
196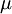
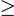 19639.2=0.2
19639.2=0.2
Two boxes are placed on top of each other on a horizontal surface as shown in the diagram. The top box has mass 5 kg and the lower box has mass 10 kg. Draw diagrams to show the forces acting on each box and calculate the magnitude of each of these forces.
Solution
A crate has mass 250 kg and rests on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the surface is 0.6. A horizontal force of magnitude
a)
b)
Solution
In this case
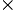 9.8=2450 N
9.8=2450 N
Hence using

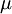 R
R
 0.6
0.6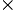 2450F
2450F 1470 N
1470 N
a) In this case
b) In this case