Introduction to forces
From Mechanics
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
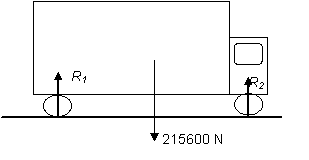
The diagram shows the lorry and its weight. | The diagram shows the lorry and its weight. | ||
| + | [[Image:truck.gif||center]] | ||
Revision as of 15:03, 13 March 2009
Newton's First Law
A particle will move with a constant velocity or remain at rest if the resultant force on the particle is zero.
Equilibrium
If the resultant force on a particle is zero, then the forces acting on the particle are said to be in equilibrium.
The Universal Law of Gravitation
\displaystyle F=\frac{Gm_{1}m_{2}}{d^{2}}
\displaystyle G=6.67\times 10^{-11}\text{ kg}^{\text{-1}}\text{m}^{\text{3}}\text{s}^{\text{-2}}
Gravity on Earth
The force of gravity is often called the weight.
\displaystyle \begin{align}
& F=mg \\
& g=9.8\text{ ms}^{\text{-2}} \\
\end{align}
Data
Radius of Earth is
\displaystyle \text{6}.\text{37}\times \text{1}0^{\text{6}}\text{ }
metres
Mass of Earth is \displaystyle \text{5}.\text{98}\times \text{1}0^{\text{24}}\text{ } kg
Describe whether or not the forces acting on the following objects are in equilibrium:
(a) A passenger in a train that travels at a constant speed.
(b) A hot air balloon rising at a constant rate.
(c) A stone dropped into a very deep well full of water.
Solution
(a) Yes, if it is travelling in a straight line.
(b) Yes, if it is travelling in a straight line.
(c) Yes, if it reaches a terminal velocity, so that it is travelling in a straight line at a constant speed.
Find the magnitude of the force of gravity (weight) acting on a lorry of mass 22 tonnes.
Solution
This is calculated using the fact that the weight is given by mg.
\displaystyle \begin{align}
& mg=22000\times 9.8 \\
& =215600\text{ N}
\end{align}
The diagram shows the lorry and its weight.
Note that reaction forces also act upwards on each wheel.
\displaystyle R_{1}+R_{2}+R_{3}+R_{4}=215600