Lösung 1.1:4
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{Displayed math +{{Abgesetzte Formel)) |
|||
| (Der Versionsvergleich bezieht 4 dazwischen liegende Versionen mit ein.) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
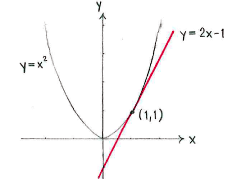
| - | + | Wir schreiben die Tangente als | |
| - | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>y=kx+m</math>}} | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>y=kx+m</math>.}} |
| - | + | Wir wissen, dass die Steigung ''k'' der Tangente die Ableitung von <math>y = x^2</math> im Punkt <math>x=1\,</math> ist, da <math>y^{\,\prime} = 2x\,</math>. | |
| - | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>k = y^{\,\prime}(1) = 2\cdot 1 = 2\,\textrm{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>k = y^{\,\prime}(1) = 2\cdot 1 = 2\,\textrm{}</math>}} |
| - | + | Wir bestimmen die Konstante ''m'' durch die Bedingung, dass die Tangente durch den Punkt (1,1) geht. | |
{{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>1 = 2\cdot 1 + m</math>}} | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>1 = 2\cdot 1 + m</math>}} | ||
| - | + | Also ist <math>m=-1</math>. | |
[[Image:1_1_4_1.gif|center]] | [[Image:1_1_4_1.gif|center]] | ||
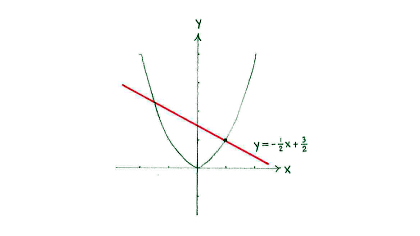
| - | + | Die Normale zu <math>y=x^2</math> im Punkt (1,1) steht senkrecht auf der Tangente im selben Punkt. | |
| - | + | Nachdem zwei senkrechte Geraden <math>k_{1}\cdot k_{2} = -1\,</math> erfüllen, hat die Normale die Steigung | |
{{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>-\frac{1}{k} = -\frac{1}{2}\,\textrm{.}</math>}} | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>-\frac{1}{k} = -\frac{1}{2}\,\textrm{.}</math>}} | ||
| - | + | Und daher ist die Normale | |
| - | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>y=-\frac{1}{2}x+n</math>}} | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>y=-\frac{1}{2}x+n</math>.}} |
| - | + | Um ''n'' zu bestimmen, verwenden wir die Bedingung, dass die Normale durch den Punkt (1,1) geht. | |
| - | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>1=-\frac{1}{2}\cdot 1 + n</math>}} | |
| - | + | Wir erhalten <math>n=\tfrac{3}{2}\,</math>. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
[[Image:1_1_4-3(3).gif|center]] | [[Image:1_1_4-3(3).gif|center]] | ||
Aktuelle Version
Wir schreiben die Tangente als
| \displaystyle y=kx+m. |
Wir wissen, dass die Steigung k der Tangente die Ableitung von \displaystyle y = x^2 im Punkt \displaystyle x=1\, ist, da \displaystyle y^{\,\prime} = 2x\,.
| \displaystyle k = y^{\,\prime}(1) = 2\cdot 1 = 2\,\textrm{} |
Wir bestimmen die Konstante m durch die Bedingung, dass die Tangente durch den Punkt (1,1) geht.
| \displaystyle 1 = 2\cdot 1 + m |
Also ist \displaystyle m=-1.
Die Normale zu \displaystyle y=x^2 im Punkt (1,1) steht senkrecht auf der Tangente im selben Punkt.
Nachdem zwei senkrechte Geraden \displaystyle k_{1}\cdot k_{2} = -1\, erfüllen, hat die Normale die Steigung
| \displaystyle -\frac{1}{k} = -\frac{1}{2}\,\textrm{.} |
Und daher ist die Normale
| \displaystyle y=-\frac{1}{2}x+n. |
Um n zu bestimmen, verwenden wir die Bedingung, dass die Normale durch den Punkt (1,1) geht.
| \displaystyle 1=-\frac{1}{2}\cdot 1 + n |
Wir erhalten \displaystyle n=\tfrac{3}{2}\,.