Lösung 3.2:1d
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K (Solution 3.2:1d moved to Lösung 3.2:1d: Robot: moved page) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| - | + | Berechnen wir den Punkt, erhalten wir direkt | |
{{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\begin{align} | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\begin{align} | ||
| Zeile 8: | Zeile 8: | ||
\end{align}</math>}} | \end{align}</math>}} | ||
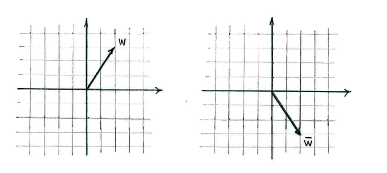
| - | + | Um den Vektor <math>\bar{w}</math> geometrisch zu deuten, müssen wir einsehen dass die komplexe Konjugation von <math>w</math> eine Spiegelung in der reellen Achse ist, nachdem der Imaginärteil durch die Kunjugation Vorzeichen tauscht. | |
[[Image:3_2_1_d1.gif|center]] | [[Image:3_2_1_d1.gif|center]] | ||
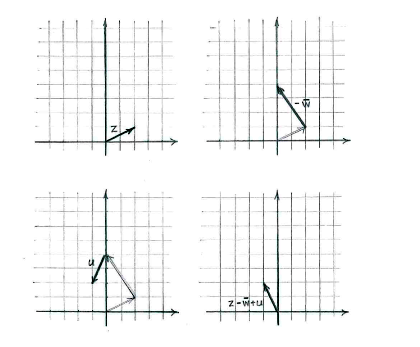
| - | + | Dadurch erhalten wir den Ausdruck einfach: | |
[[Image:3_2_1d-2(2).gif|center]] | [[Image:3_2_1d-2(2).gif|center]] | ||
Version vom 18:43, 12. Mai 2009
Berechnen wir den Punkt, erhalten wir direkt
| \displaystyle \begin{align}
z-\bar{w}+u &= (2+i)-(2-3i)+(-1-2i)\\[5pt] &= 2-2-1+(1+3-2)i\\[5pt] &= -1+2i\,\textrm{.} \end{align} |
Um den Vektor \displaystyle \bar{w} geometrisch zu deuten, müssen wir einsehen dass die komplexe Konjugation von \displaystyle w eine Spiegelung in der reellen Achse ist, nachdem der Imaginärteil durch die Kunjugation Vorzeichen tauscht.
Dadurch erhalten wir den Ausdruck einfach: