Lösung 2.1:1d
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
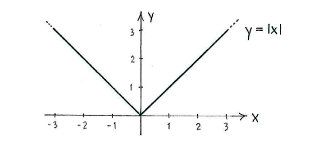
The modulus function, \displaystyle |x|, strips \displaystyle x of its sign, e.g.
| \displaystyle |-5|=5\,, \displaystyle \quad|3|=3\quad and \displaystyle \quad |-\pi|=\pi\,. |
For positive values of \displaystyle x, the modulus function has no effect, since \displaystyle |x|=x, but for negative \displaystyle x the modulus function changes the sign of \displaystyle x, i.e. \displaystyle |x|=-x (remember that \displaystyle x is negative and therefore \displaystyle -x is positive).
If we draw a graph of \displaystyle y=|x| it will consist of two parts. For \displaystyle x\ge 0 we have \displaystyle y=x, and for \displaystyle x\le 0 we have \displaystyle y=-x\,.
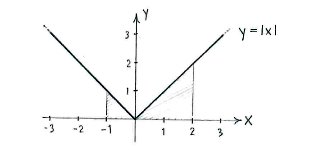
The value of the integral is the area of the region under the graph \displaystyle y=|x| and between \displaystyle x=-1 and \displaystyle x=2.
This region consists of two triangles and we therefore obtain
| \displaystyle \int\limits_{-1}^{2} |x|\,dx = \frac{1}{2}\cdot 1\cdot 1 + \frac{1}{2}\cdot 2\cdot 2 = \frac{5}{2}\,\textrm{.} |