Lösung 1.1:5
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
K |
K (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{Displayed math +{{Abgesetzte Formel)) |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
Suppose that the tangent touches the curve at the point <math>(x_0,y_0)</math>. That point must, first and foremost, lie on the curve and therefore satisfy the equation of the curve, i.e. | Suppose that the tangent touches the curve at the point <math>(x_0,y_0)</math>. That point must, first and foremost, lie on the curve and therefore satisfy the equation of the curve, i.e. | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>y_0 = -x_0^2\,\textrm{.}</math>|(1)}} |
If we now write the equation of the tangent as <math>y=kx+m</math>, the slope of the tangent, ''k'', is given by the value of the curve's derivative, <math>y^{\,\prime} = -2x</math>, at <math>x=x_0</math>, | If we now write the equation of the tangent as <math>y=kx+m</math>, the slope of the tangent, ''k'', is given by the value of the curve's derivative, <math>y^{\,\prime} = -2x</math>, at <math>x=x_0</math>, | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>k = -2x_0\,\textrm{.}</math>|(2)}} |
The condition that the tangent goes through the point <math>(x_0,y_0)</math> gives us that | The condition that the tangent goes through the point <math>(x_0,y_0)</math> gives us that | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>y_{0} = k\cdot x_0 + m\,\textrm{.}</math>|(3)}} |
In addition to this, the tangent should also pass through the point (1,1), | In addition to this, the tangent should also pass through the point (1,1), | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>1 = k\cdot 1 + m\,\textrm{.}</math>|(4)}} |
Equations (1)-(4) constitute a system of equations in the unknowns <math>x_0</math>, <math>y_{0}</math>, <math>k</math> and <math>m</math>. | Equations (1)-(4) constitute a system of equations in the unknowns <math>x_0</math>, <math>y_{0}</math>, <math>k</math> and <math>m</math>. | ||
| Zeile 21: | Zeile 21: | ||
Equation (2) gives that <math>k = -2 x_0</math> and substituting this into equation (4) gives | Equation (2) gives that <math>k = -2 x_0</math> and substituting this into equation (4) gives | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>1 = -2x_0 + m\quad\Leftrightarrow\quad m = 2x_0+1\,\textrm{.}</math>}} |
With ''k'' and ''m'' expressed in terms of <math>x_0</math> and <math>y_0</math>, (3) becomes an equation that is expressed completely in terms of <math>x_0</math> | With ''k'' and ''m'' expressed in terms of <math>x_0</math> and <math>y_0</math>, (3) becomes an equation that is expressed completely in terms of <math>x_0</math> | ||
and <math>y_0</math>, | and <math>y_0</math>, | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>y_0 = -2x_0^2 + 2x_0 + 1\,\textrm{.}</math>|(3')}} |
This equation, together with (1), is a system of equations in <math>x_0</math> and <math>y_0</math>, | This equation, together with (1), is a system of equations in <math>x_0</math> and <math>y_0</math>, | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\left\{\begin{align} |
y_{0} &= -x_0^{2}\,,\\[5pt] | y_{0} &= -x_0^{2}\,,\\[5pt] | ||
y_{0} &= -2x_0^2 + 2x_0 + 1\,\textrm{.} | y_{0} &= -2x_0^2 + 2x_0 + 1\,\textrm{.} | ||
| Zeile 37: | Zeile 37: | ||
Substituting equation (1) into (3') gives us an equation in <math>x_0</math>, | Substituting equation (1) into (3') gives us an equation in <math>x_0</math>, | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>-x_0^2 = -2x_0^2 + 2x_0 + 1\,,</math>}} |
i.e. | i.e. | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>x_0^2 - 2x_0 - 1 = 0\,\textrm{.}</math>}} |
This quadratic equation has solutions | This quadratic equation has solutions | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>x_0 = 1-\sqrt{2}\qquad\text{and}\qquad x_0 = 1+\sqrt{2}\,\textrm{.}</math>}} |
Equation (1) gives the corresponding y-values, | Equation (1) gives the corresponding y-values, | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>y_0 = -3+2\sqrt{2}\qquad\text{and}\qquad y_0 = -3-2\sqrt{2}\,\textrm{.}</math>}} |
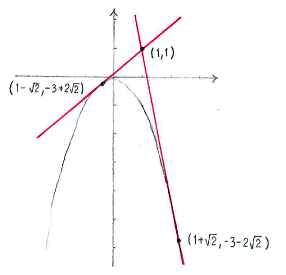
Thus, the answers are the points <math>(1-\sqrt{2},-3+2\sqrt{2})</math> and | Thus, the answers are the points <math>(1-\sqrt{2},-3+2\sqrt{2})</math> and | ||
Version vom 12:51, 10. Mär. 2009
Suppose that the tangent touches the curve at the point \displaystyle (x_0,y_0). That point must, first and foremost, lie on the curve and therefore satisfy the equation of the curve, i.e.
| \displaystyle y_0 = -x_0^2\,\textrm{.} | (1) |
If we now write the equation of the tangent as \displaystyle y=kx+m, the slope of the tangent, k, is given by the value of the curve's derivative, \displaystyle y^{\,\prime} = -2x, at \displaystyle x=x_0,
| \displaystyle k = -2x_0\,\textrm{.} | (2) |
The condition that the tangent goes through the point \displaystyle (x_0,y_0) gives us that
| \displaystyle y_{0} = k\cdot x_0 + m\,\textrm{.} | (3) |
In addition to this, the tangent should also pass through the point (1,1),
| \displaystyle 1 = k\cdot 1 + m\,\textrm{.} | (4) |
Equations (1)-(4) constitute a system of equations in the unknowns \displaystyle x_0, \displaystyle y_{0}, \displaystyle k and \displaystyle m.
Because we are looking for \displaystyle x_0 and \displaystyle y_0, the first step is to try and eliminate k and m from the equations.
Equation (2) gives that \displaystyle k = -2 x_0 and substituting this into equation (4) gives
| \displaystyle 1 = -2x_0 + m\quad\Leftrightarrow\quad m = 2x_0+1\,\textrm{.} |
With k and m expressed in terms of \displaystyle x_0 and \displaystyle y_0, (3) becomes an equation that is expressed completely in terms of \displaystyle x_0 and \displaystyle y_0,
| \displaystyle y_0 = -2x_0^2 + 2x_0 + 1\,\textrm{.} | (3') |
This equation, together with (1), is a system of equations in \displaystyle x_0 and \displaystyle y_0,
| \displaystyle \left\{\begin{align}
y_{0} &= -x_0^{2}\,,\\[5pt] y_{0} &= -2x_0^2 + 2x_0 + 1\,\textrm{.} \end{align}\right. |
Substituting equation (1) into (3') gives us an equation in \displaystyle x_0,
| \displaystyle -x_0^2 = -2x_0^2 + 2x_0 + 1\,, |
i.e.
| \displaystyle x_0^2 - 2x_0 - 1 = 0\,\textrm{.} |
This quadratic equation has solutions
| \displaystyle x_0 = 1-\sqrt{2}\qquad\text{and}\qquad x_0 = 1+\sqrt{2}\,\textrm{.} |
Equation (1) gives the corresponding y-values,
| \displaystyle y_0 = -3+2\sqrt{2}\qquad\text{and}\qquad y_0 = -3-2\sqrt{2}\,\textrm{.} |
Thus, the answers are the points \displaystyle (1-\sqrt{2},-3+2\sqrt{2}) and \displaystyle (1+\sqrt{2},-3-2\sqrt{2})\,.