Lösung 2.1:1b
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
| (Der Versionsvergleich bezieht 4 dazwischen liegende Versionen mit ein.) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
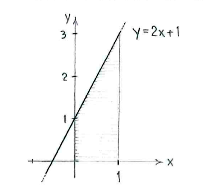
| - | + | Die Funktion <math>y=2x+1</math> ist eine Gerade, die die ''y''-Achse in <math>y=1</math> schneidet und die Steigung 2 hat. | |
| - | <math>y=2x+1</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | - | + | |
| - | <math>y= | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | Das Integral entspricht der Fläche unter der Geraden zwischen <math>x=0</math> | ||
| + | und <math>x=1</math>. | ||
[[Image:2_1_1_b1.gif|center]] | [[Image:2_1_1_b1.gif|center]] | ||
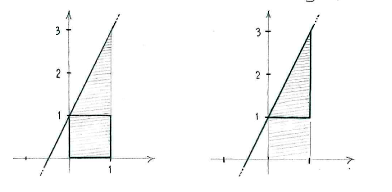
| - | + | Wir teilen die Fläche in zwei Teilflächen auf, ein Rechteck und ein Dreieck | |
| - | + | ||
[[Image:2_1_1_b2.gif|center]] | [[Image:2_1_1_b2.gif|center]] | ||
| - | + | und addieren deren Flächen, um die gesamte Fläche zu bekommen. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | Das Integral ist daher | ||
| - | <math>\int\limits_{0}^{1} | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\begin{align} |
| - | ( | + | \int\limits_{0}^{1} (2x+1)\,dx |
| - | + | &= \text{(Fläche des Rechtecks)} + \text{(Fläche des Dreiecks)}\\ | |
| + | &= 1\cdot 1 + \frac{1}{2}\cdot 1\cdot 2 = 2\,\textrm{.} | ||
| + | \end{align}</math>}} | ||
Aktuelle Version
Die Funktion \displaystyle y=2x+1 ist eine Gerade, die die y-Achse in \displaystyle y=1 schneidet und die Steigung 2 hat.
Das Integral entspricht der Fläche unter der Geraden zwischen \displaystyle x=0 und \displaystyle x=1.
Wir teilen die Fläche in zwei Teilflächen auf, ein Rechteck und ein Dreieck
und addieren deren Flächen, um die gesamte Fläche zu bekommen.
Das Integral ist daher
| \displaystyle \begin{align}
\int\limits_{0}^{1} (2x+1)\,dx &= \text{(Fläche des Rechtecks)} + \text{(Fläche des Dreiecks)}\\ &= 1\cdot 1 + \frac{1}{2}\cdot 1\cdot 2 = 2\,\textrm{.} \end{align} |