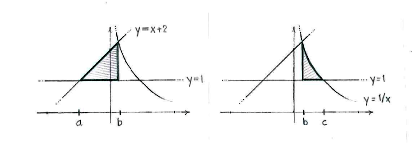Lösung 2.1:4d
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
We start by drawing the three curves:
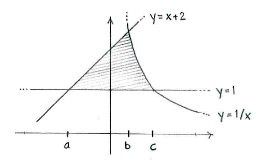
When we draw the curves on the same diagram, we see that the region is bounded from below in the \displaystyle y -direction by the horizontal line \displaystyle y=\text{1} and above partly by \displaystyle y=x+2 and partly by \displaystyle y=\frac{1}{x}.
If we denote the \displaystyle x -coordinates of the intersection points by \displaystyle x=a, \displaystyle x=b and \displaystyle x=c, as shown in the figure, we see that the region can be divided up into two parts. In the left part between \displaystyle x=a and \displaystyle x=b, the upper limit is \displaystyle y=x+2, whilst in the right part between \displaystyle x=b and \displaystyle x=c
\displaystyle y={1}/{x}\; is the upper limit.
The area of each part is given by the integrals
Left area \displaystyle =\int\limits_{a}^{b}{\left( x+2-1 \right)}\,dx
Right area
\displaystyle =\int\limits_{b}^{c}{\left( \frac{1}{x}-1 \right)}\,dx
and the total area is the sum of these areas.
If we just manage to determine the curves' points of intersection, the rest is just a matter of integration.
To determine the points of intersection:
\displaystyle x=a: the point of intersection between
\displaystyle y=\text{1 }
and
\displaystyle y=x+\text{2}
must both satisfy the equations of the lines
\displaystyle \left\{ \begin{matrix}
y=\text{1 } \\
y=x+\text{2} \\
\end{matrix} \right.
This gives that
\displaystyle x
must satisfy
\displaystyle x+\text{2}=\text{1}, i.e.
\displaystyle x=-\text{1 }
Thus,
\displaystyle a=-\text{1}.
\displaystyle x=b: At the point where the curves
\displaystyle y=x+\text{2}
and
\displaystyle y={1}/{x}\;
meet, we have that
\displaystyle \left\{ \begin{matrix}
y=x+\text{2} \\
y={1}/{x}\; \\
\end{matrix} \right.
If we eliminate
\displaystyle y, we obtain an equation for
\displaystyle x,
\displaystyle x+2=\frac{1}{x},
which we multiply by \displaystyle x,
\displaystyle x^{2}+2x=1
Completing the square of the left-hand side,
\displaystyle \begin{align}
& \left( x+1 \right)^{2}-1^{2}=1 \\
& \left( x+1 \right)^{2}=2 \\
\end{align},
and taking the root gives that \displaystyle x=-1\pm \sqrt{2}, leading to \displaystyle b=-1+\sqrt{2}
(the alternative \displaystyle b=-1-\sqrt{2} lies to the left of \displaystyle b=a).
\displaystyle x=c: the final point of intersection is given by the condition that the equation to both curves,
\displaystyle y=\text{1}
and
\displaystyle y={1}/{x}\;, are satisfied simultaneously. We see almost immediately that this gives
\displaystyle x=\text{1}, i.e.
\displaystyle c=\text{ 1}.
The sub-areas are
\displaystyle \begin{align}
& \text{Leftarea }=\text{ }\int\limits_{-1}^{\sqrt{2}-1}{\left( x+2-1 \right)}\,dx=\int\limits_{-1}^{\sqrt{2}-1}{\left( x+1 \right)}\,dx \\
& =\left[ \frac{x^{2}}{2}+x \right]_{-1}^{\sqrt{2}-1} \\
& =\frac{\left( \sqrt{2}-1 \right)^{2}}{2}+\sqrt{2}-1-\left( \frac{\left( -1 \right)^{2}}{2}+\left( -1 \right) \right) \\
& =\frac{\left( \sqrt{2} \right)^{2}-2\sqrt{2}+1}{2}+\sqrt{2}-1-\frac{1}{2}+1 \\
& =\frac{2-2\sqrt{2}+1}{2}+\sqrt{2}-1-\frac{1}{2}+1 \\
& =1-\sqrt{2}+\frac{1}{2}+\sqrt{2}-1-\frac{1}{2}+1 \\
& =1 \\
\end{align}
\displaystyle \begin{align} & \text{Rightarea }=\int\limits_{\sqrt{2}-1}^{1}{\left( \frac{1}{x}-1 \right)}\,dx=\left[ \ln \left| x \right|-x \right]_{\sqrt{2}-1}^{1} \\ & =\ln 1-1-\left( \ln \left( \sqrt{2}-1 \right)-\left( \sqrt{2}-1 \right) \right) \\ & =0-1-\ln \left( \sqrt{2}-1 \right)+\sqrt{2}-1 \\ & =\sqrt{2}-2-\ln \left( \sqrt{2}-1 \right) \\ \end{align}