Lösung 1.3:1b
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
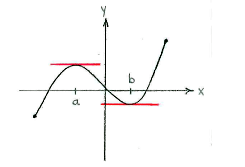
There are two points, \displaystyle x=a and \displaystyle x=b (see picture below), where the function has a horizontal tangent and hence a derivative equal to zero. These are the functions critical points.
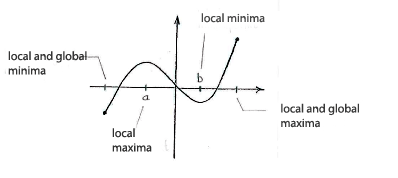
Furthermore, we see that the function has local minimum points at the left endpoint of the interval of definition and \displaystyle x=b, because the function takes higher values at neighbouring points. In the same way, we see that the function has local maximum points at \displaystyle x=a and at the right endpoint of the interval of definition.
Of these local extreme points, the left endpoint is a global minimum (that point where the function takes its absolute minimum value) and the right endpoint is a global maximum.
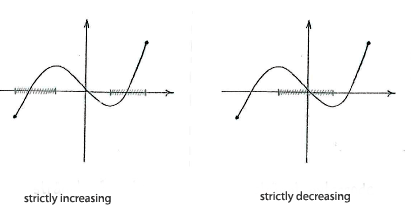
The function is strictly increasing (it has a tangent that slopes upwards) in the interval between the left endpoint and \displaystyle x=a, as well as between \displaystyle x=b and the right endpoint. In the interval between \displaystyle x=0 and \displaystyle x=b, the function is strictly decreasing.