Lösung 2.1:1b
Aus Online Mathematik Brückenkurs 2
(Unterschied zwischen Versionen)
K |
K (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{Displayed math +{{Abgesetzte Formel)) |
||
| Zeile 14: | Zeile 14: | ||
The value of the integral is | The value of the integral is | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{Abgesetzte Formel||<math>\begin{align} |
\int\limits_{0}^{1} (2x+1)\,dx | \int\limits_{0}^{1} (2x+1)\,dx | ||
&= \text{(area of the square)} + \text{(area of the triangle)}\\ | &= \text{(area of the square)} + \text{(area of the triangle)}\\ | ||
&= 1\cdot 1 + \frac{1}{2}\cdot 1\cdot 2 = 2\,\textrm{.} | &= 1\cdot 1 + \frac{1}{2}\cdot 1\cdot 2 = 2\,\textrm{.} | ||
\end{align}</math>}} | \end{align}</math>}} | ||
Version vom 12:57, 10. Mär. 2009
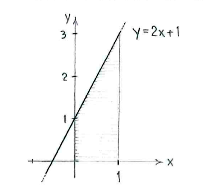
The graph of the function \displaystyle y=2x+1 is a straight line which cuts the y-axis at \displaystyle y=1 and has slope 2.
The integral's value is the area under the straight line and between \displaystyle x=0 and \displaystyle x=1.
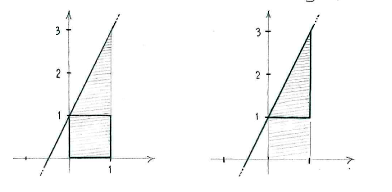
We can divide up the region under the graph into a square and rectangle,
and then add up the area to obtain the total area.
The value of the integral is
| \displaystyle \begin{align}
\int\limits_{0}^{1} (2x+1)\,dx &= \text{(area of the square)} + \text{(area of the triangle)}\\ &= 1\cdot 1 + \frac{1}{2}\cdot 1\cdot 2 = 2\,\textrm{.} \end{align} |